See full article for more information
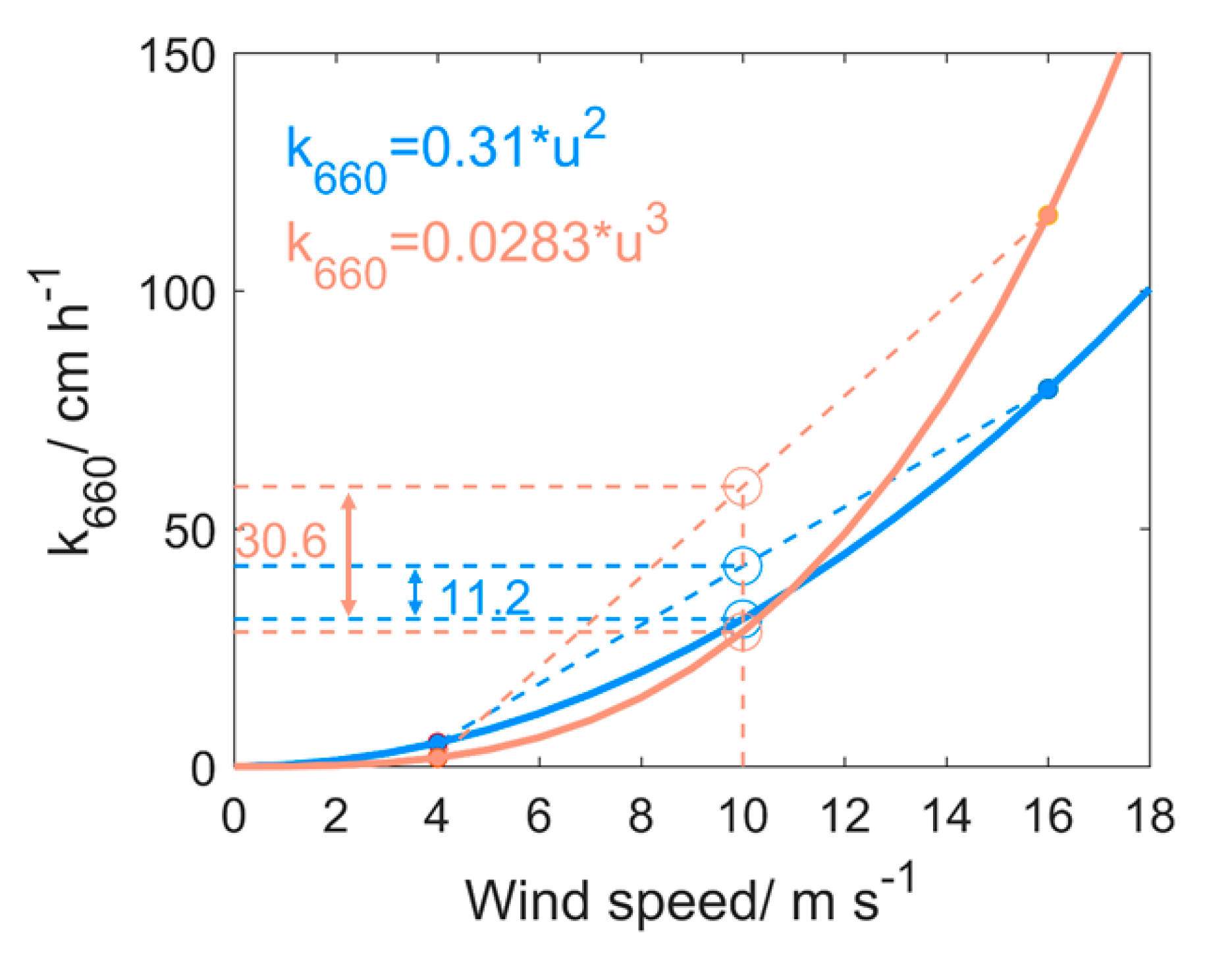
The significance of the water-side gas transfer velocity for air–sea CO2 gas exchange (k) and its non-linear dependence on wind speed (U) is well accepted. What remains a subject of inquiry are biases associated with the form of the non-linear relation linking k to U (hereafter labeled as f(U), where f(.) stands for an arbitrary function of U), the distributional properties of U (treated as a random variable) along with other external factors influencing k, and the time-averaging period used to determine k from U. To address the latter issue, a Taylor series expansion is applied to separate f(U) into a term derived from time-averaging wind speed (labeled as ⟨U⟩, where ⟨.⟩ indicates averaging over a monthly time scale) as currently employed in climate models and additive bias corrections that vary with the statistics of U. The method was explored for nine widely used f(U) parameterizations based on remotely-sensed 6-hourly global wind products at 10 m above the sea-surface. The bias in k of monthly estimates compared to the reference 6-hourly product was shown to be mainly associated with wind variability captured by the standard deviation σσU around ⟨U⟩ or, more preferably, a dimensionless coefficient of variation Iu= σσU/⟨U⟩. The proposed correction outperforms previous methodologies that adjusted k when using ⟨U⟩ only. An unexpected outcome was that upon setting I2u = 0.15 to correct biases when using monthly wind speed averages, the new model produced superior results at the global and regional scale compared to prior correction methodologies. Finally, an equation relating I2u to the time-averaging interval (spanning from 6 h to a month) is presented to enable other sub-monthly averaging periods to be used. While the focus here is on CO2, the theoretical tactic employed can be applied to other slightly soluble gases. As monthly and climatological wind data are often used in climate models for gas transfer estimates, the proposed approach provides a robust scheme that can be readily implemented in current climate models