The biodiversity of phytoplankton is a core measurement of the state and activity of marine ecosystems. In the context of historical approaches, we review recent major advances in the technologies that have enabled deeper characterization of the biodiversity of phytoplankton. In particular, high-throughput sequencing of single loci/genes, genomes, and communities (metagenomics) has revealed exceptional phylogenetic and genomic diversity whose breadth is not fully constrained. Other molecular tools—such as fingerprinting, quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and fluorescence in situ hybridization—have provided additional insight into the dynamics of this diversity in the context of environmental variability. Techniques for characterizing the functional diversity of community structure through targeted or untargeted approaches based on RNA or protein have also greatly advanced. A wide range of techniques is now available for characterizing phytoplankton communities, and these tools will continue to advance through ongoing improvements in both technology and data interpretation.
You may also like
While planktonic microbes play key roles in the coastal oceans, our understanding of heterotrophic microeukaryotes’ ecology, particularly their spatiotemporal patterns, drivers, and […]
The decarbonization of agriculture faces many challenges and has received a level of attention insufficient to abate the worst effects of climate […]
By mid-century, society will need to significantly intensify the output of its food production system while simultaneously reducing that system’s detrimental impacts […]
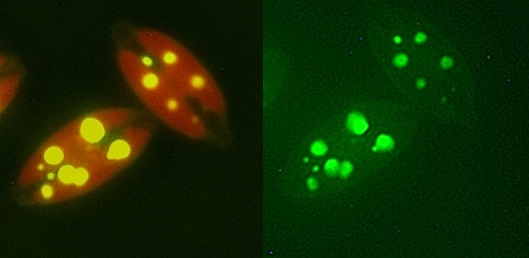
The fluorescent stain Nile Red has been used extensively for the quantification of lipids in phytoplankton, including microalgae, because it preferentially stains […]